Patcher Update
Starting in 0.4.1, Patcher applies patches using a Docker sandbox by default and pulls the latest version of the gruntwork/patcher_bash_env image.
To run Patcher locally without Docker or in a CI pipeline, use the --skip-container-runtime flag.
The patcher update command updates some or all module dependencies in the current folder and any child folders.
Patcher supports two modes: interactive mode and non-interactive mode.
Interactive mode
In interactive mode, the patcher update command allows you to selectively update dependencies one module at a time.
Example usage:
patcher update prod
After scanning for dependencies, Patcher displays the 'Modules View'.
- If all dependencies are up to date, Patcher displays a checkmark in the "Up to date" column.
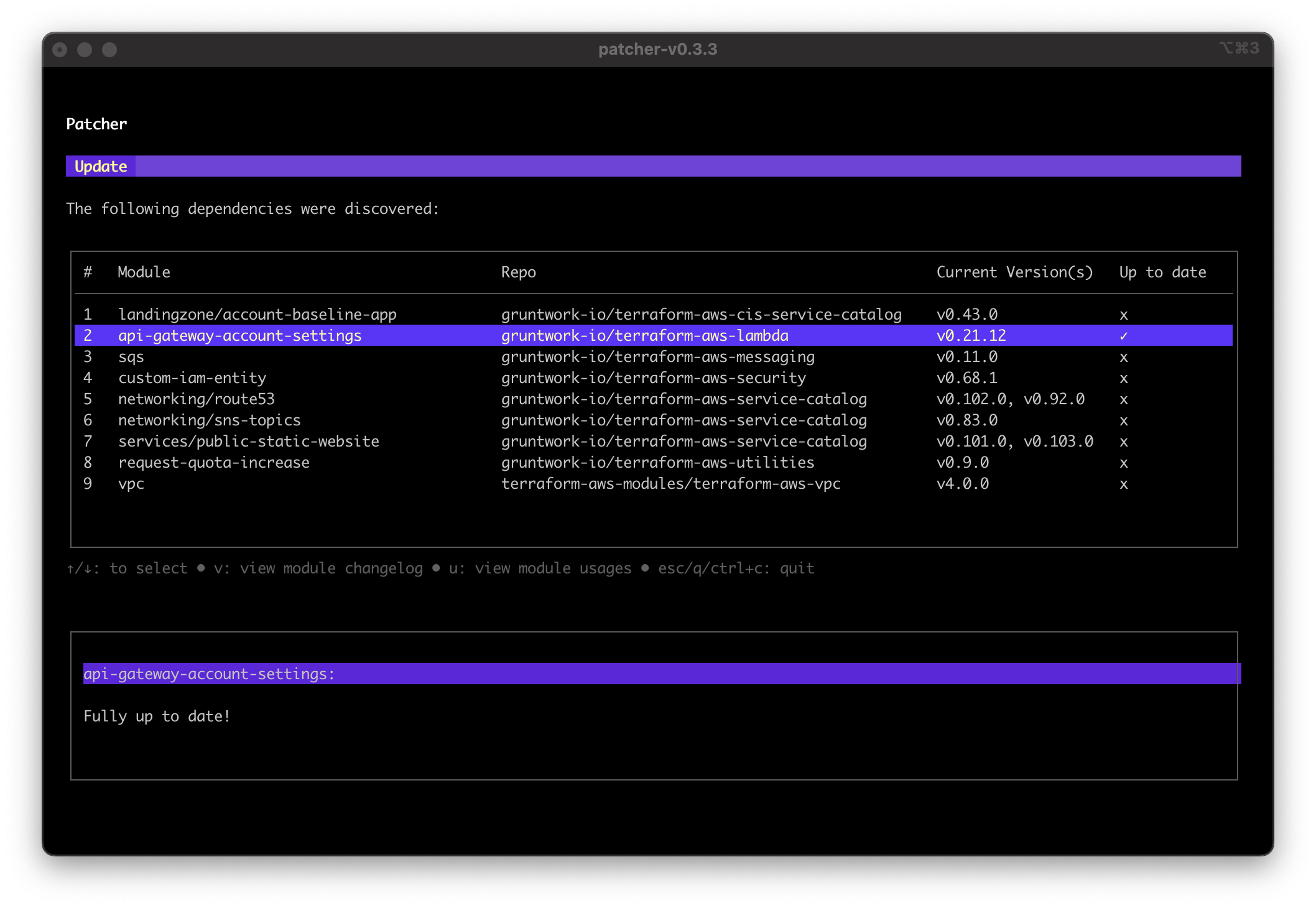 Patcher update screenshot showing dependency that is fully up to date
Patcher update screenshot showing dependency that is fully up to date
-
If Patcher detects updates, it offers two options:
- Press
ENTERto update all usages to the next safe version. - Press
bto update all usages to the next version, including breaking changes.
- Press
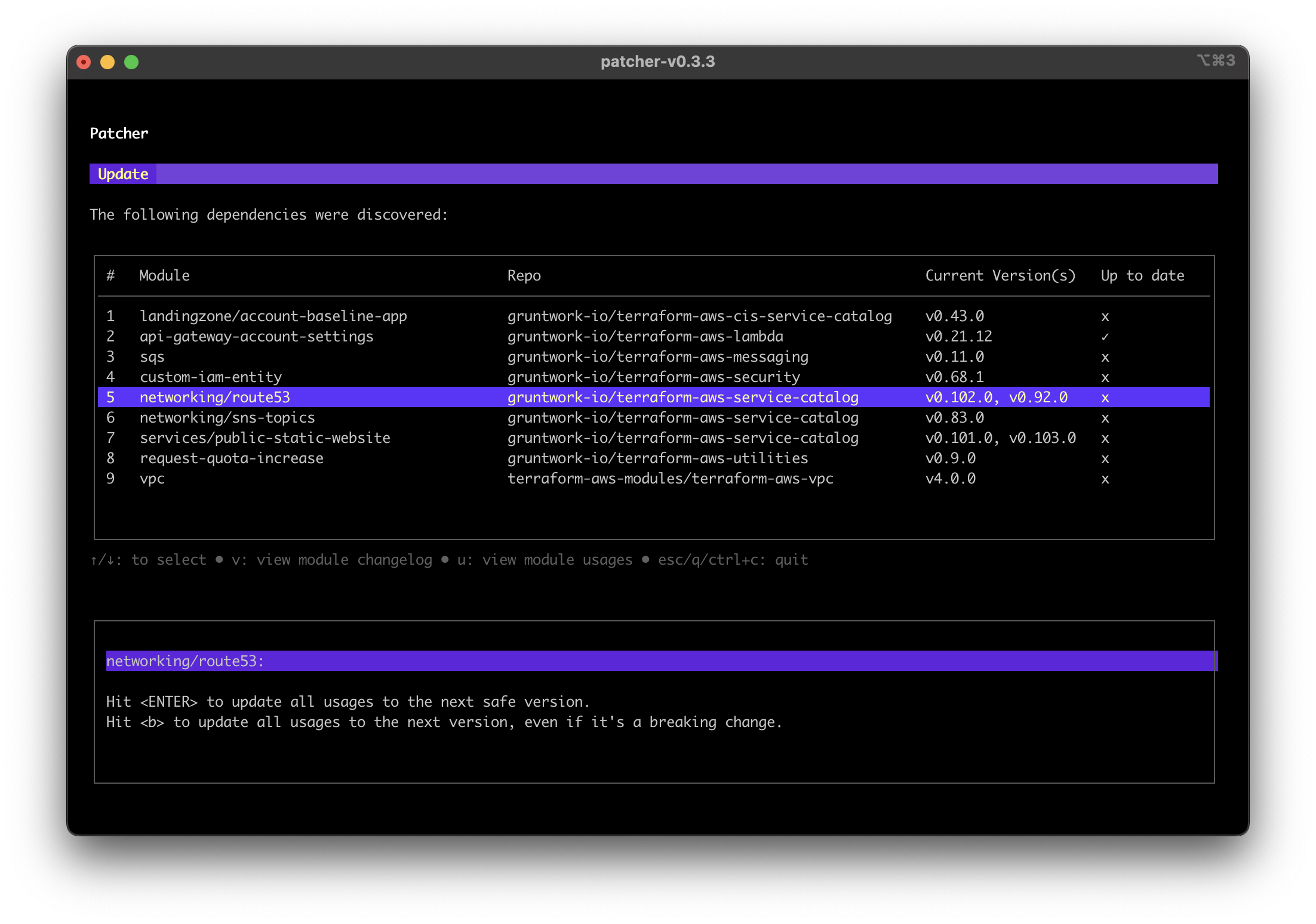 Patcher update screenshot showing dependency that can be updated
Patcher update screenshot showing dependency that can be updated
- Pressing
ENTERupdates to the highest version before the next breaking change or to the latest version, whichever comes first. - Pressing
bupdates to the next breaking change or the latest version, whichever comes first.
After updating, the "Up to date" column changes to "Updated", indicating that at least one dependency has been updated.
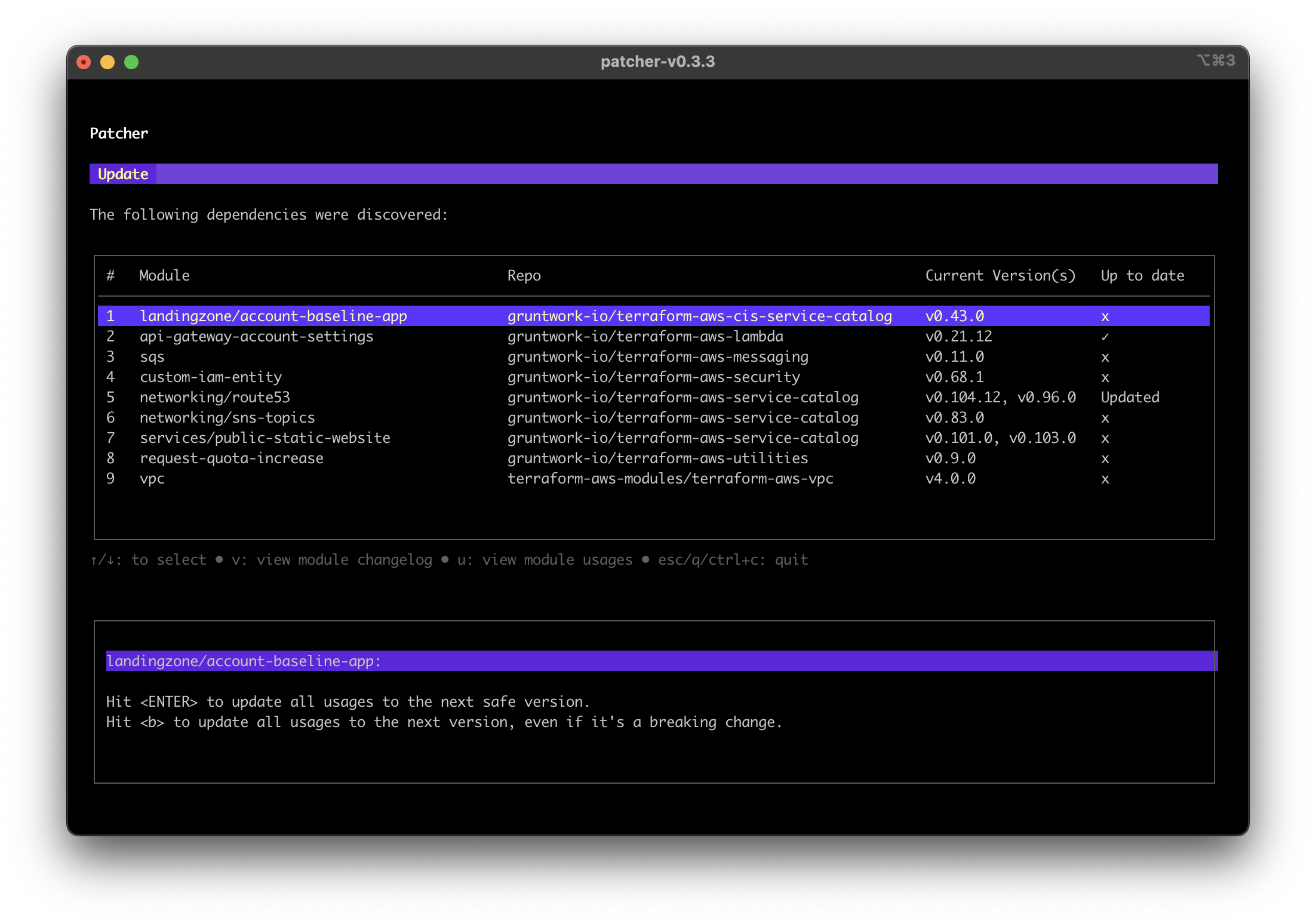 Patcher update screenshot showing dependency that has been updated
Patcher update screenshot showing dependency that has been updated
When you exit Patcher, it writes the update details to stdout in YAML format:
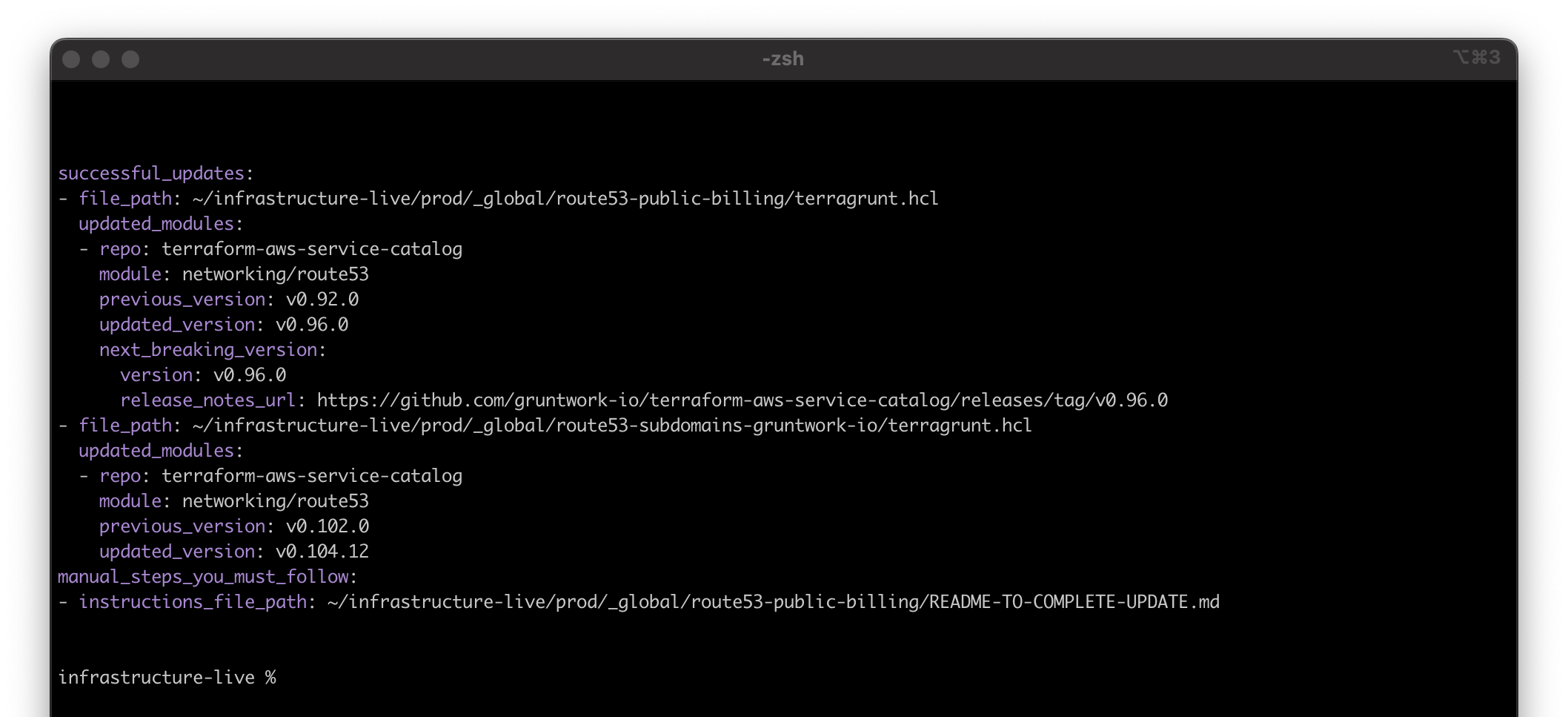 Patcher update screenshot showing YAML output
Patcher update screenshot showing YAML output
Navigation commands
- While in the modules view, press
uto display the usages. This shows all locations where the module is being used:
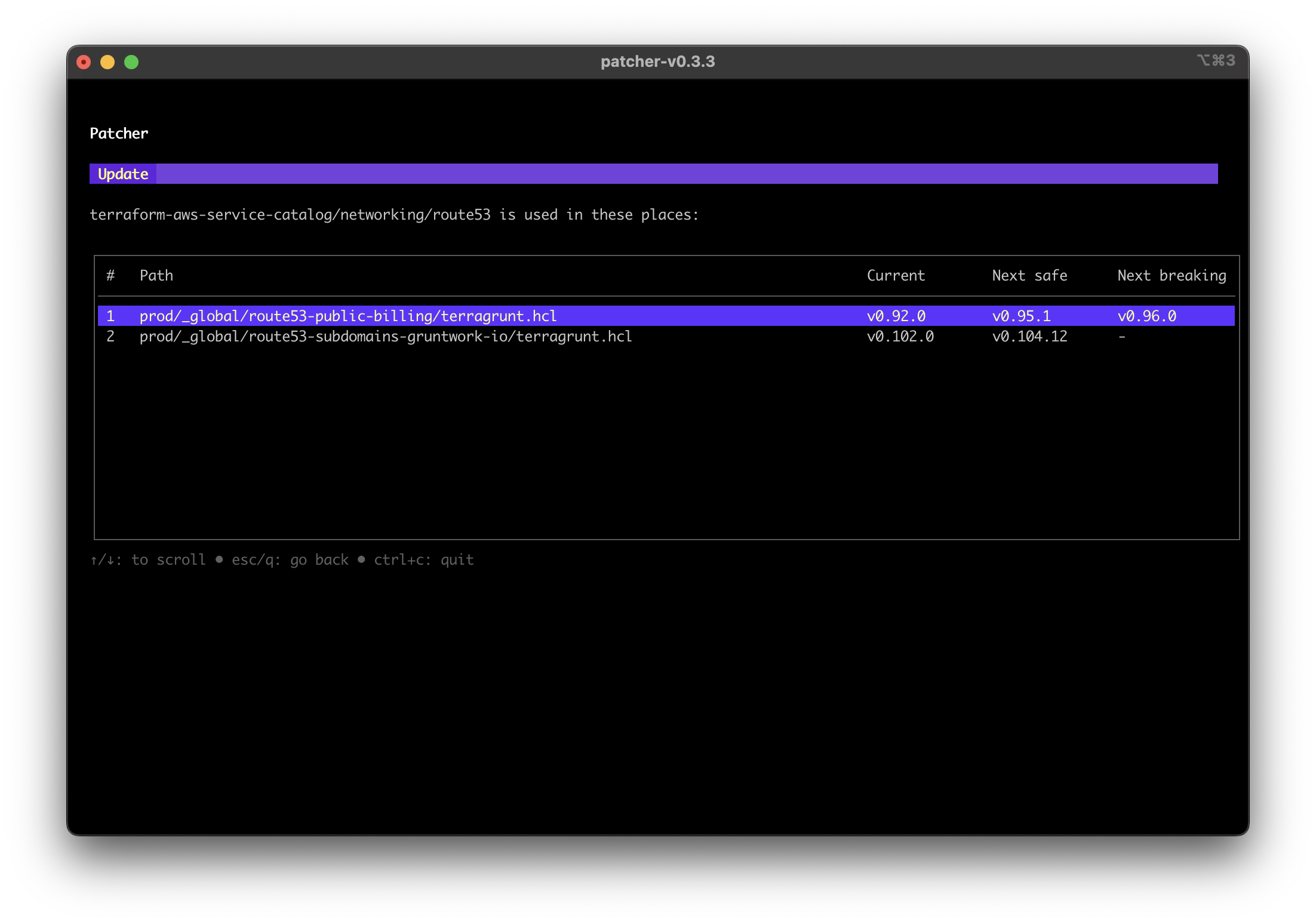 Patcher usages screenshot showing module with multiple usages
Patcher usages screenshot showing module with multiple usages
- While in the modules view, press
vto view the changelogs for a module. Pressoto open the changelog page in your browser.
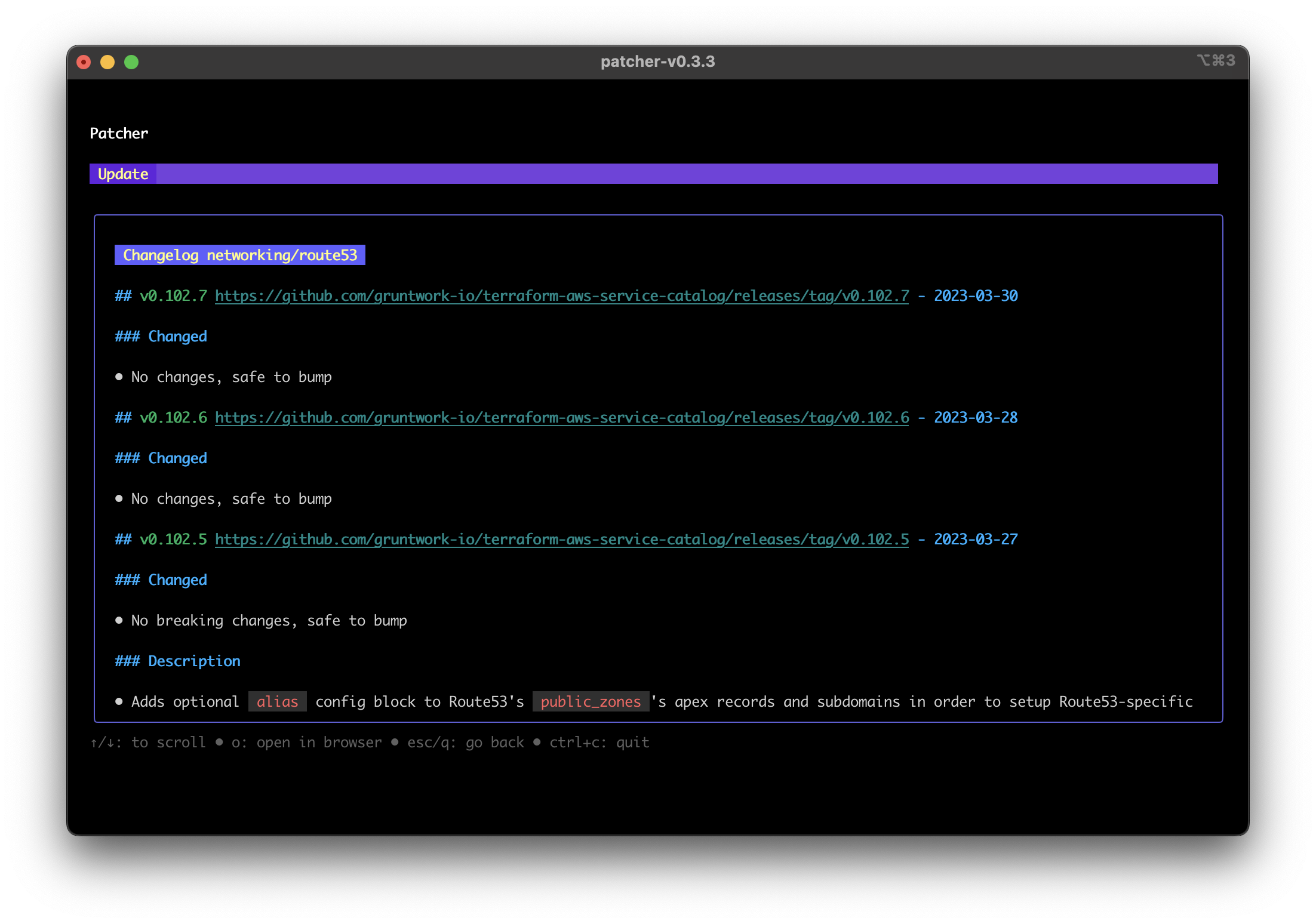 Patcher changelogs screenshot
Patcher changelogs screenshot
If a module, including third-party modules, does not have a CHANGELOG.md file, press o to open the repository's releases page.
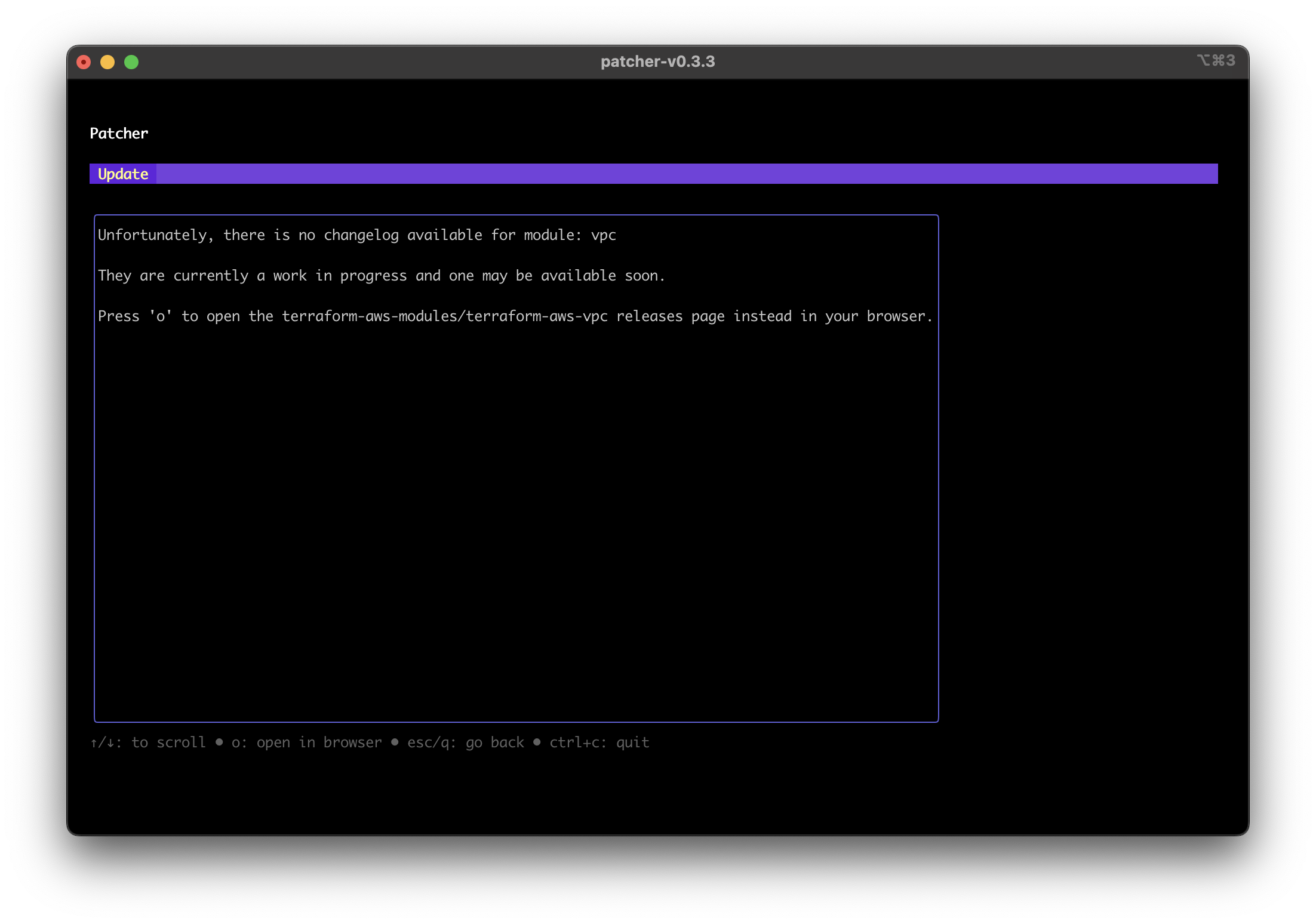 Patcher no changelogs screenshot
Patcher no changelogs screenshot
Non-interactive mode
In non-interactive mode, Patcher updates all module dependencies in the current folder (and child folders) based on the specified update strategy.
Non-interactive mode supports the next-safe and next-breaking update strategies.
Next safe (default)
Using the next safe update strategy, Patcher updates dependencies to the highest version before the next breaking change. If no breaking changes are found, it updates to the latest version of the module.
Example usage:
patcher update --non-interactive --skip-container-runtime --update-strategy next-safe prod
Or just
patcher update --non-interactive --skip-container-runtime prod
Next breaking
With the next breaking update strategy, Patcher updates dependencies to the version containing the breaking change and then stops. If no breaking changes are encountered, it updates to the latest version of the module.
If Patcher updates a dependency to a breaking version, it generates a README-TO-COMPLETE-UPDATE.md file in the folder containing the dependency. This file includes a release note extract for each dependency in that folder that was updated to a breaking change.
Example usage:
patcher update --non-interactive --skip-container-runtime --update-strategy next-breaking prod
Support for third-party modules
Patcher provides full support for third-party modules in both interactive and non-interactive modes, including your own custom modules.
Starting in 0.4.3, Patcher updates third-party modules based on semantic versioning (semver).
For example, the terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-vpc module has three recent versions: 5.0.0, 5.1.0, and 5.1.1.
In the infrastructure-live/dev environment, there is a dependency on terraform-aws-vpc/vpc:
dev/us-east-1/prod/dev/terragrunt.hclcurrently uses version4.0.0.
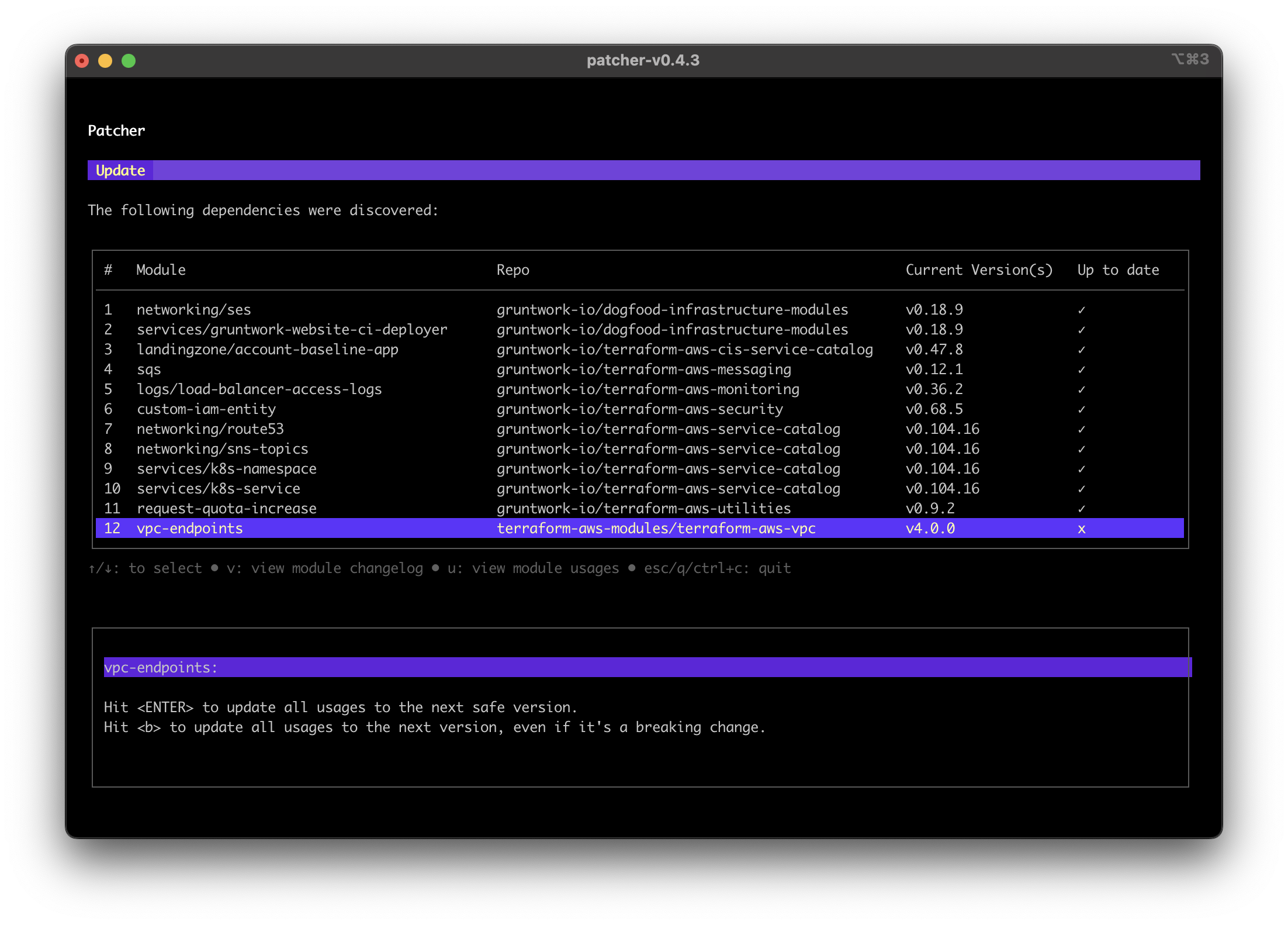 Screenshot of third party module dependency with updates available
Screenshot of third party module dependency with updates available
Patcher updates this dependency to 5.0.0 because it is the next version containing a breaking change. It also generates a README-TO-COMPLETE-UPDATE.md file in the folder containing the dependency.
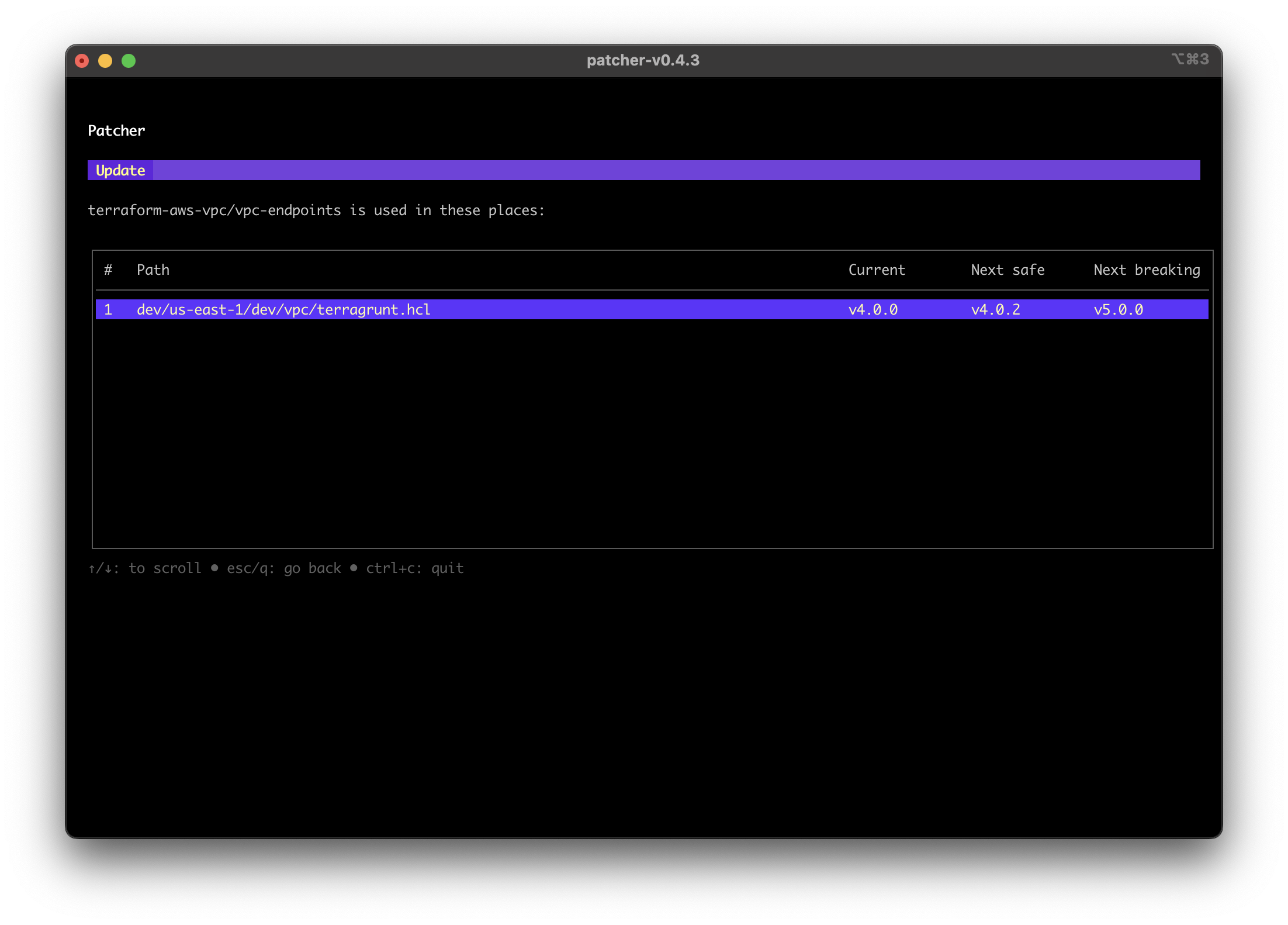 Screenshot of third party module dependency usages with updates available
Screenshot of third party module dependency usages with updates available
The README-TO-COMPLETE-UPDATE.md file includes the release notes.
# vpc-endpoints v4.0.0 -> v5.0.0 (2023.08.15 13:39:56)
Updated dependency `vpc-endpoints` in `dev/us-east-1/dev/vpc/terragrunt.hcl` to version `v5.0.0`, which includes breaking changes. You MUST follow the instructions in the release notes to complete this update safely: https://github.com/terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-vpc/releases/tag/v5.0.0
Here are the release notes for version `v5.0.0`:
## [5.0.0](https://github.com/terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-vpc/compare/v4.0.2...v5.0.0) (2023-05-30)
### ⚠ BREAKING CHANGES
* Bump Terraform AWS Provider version to 5.0 (#941)
### Features
* Bump Terraform AWS Provider version to 5.0 ([#941](https://github.com/terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-vpc/issues/941)) ([2517eb9](https://github.com/terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-vpc/commit/2517eb98a39500897feecd27178994055ee2eb5e))
Running Patcher again will complete the update to 5.1.1, the README-TO-COMPLETE-UPDATE.md file should be read, followed and deleted first.
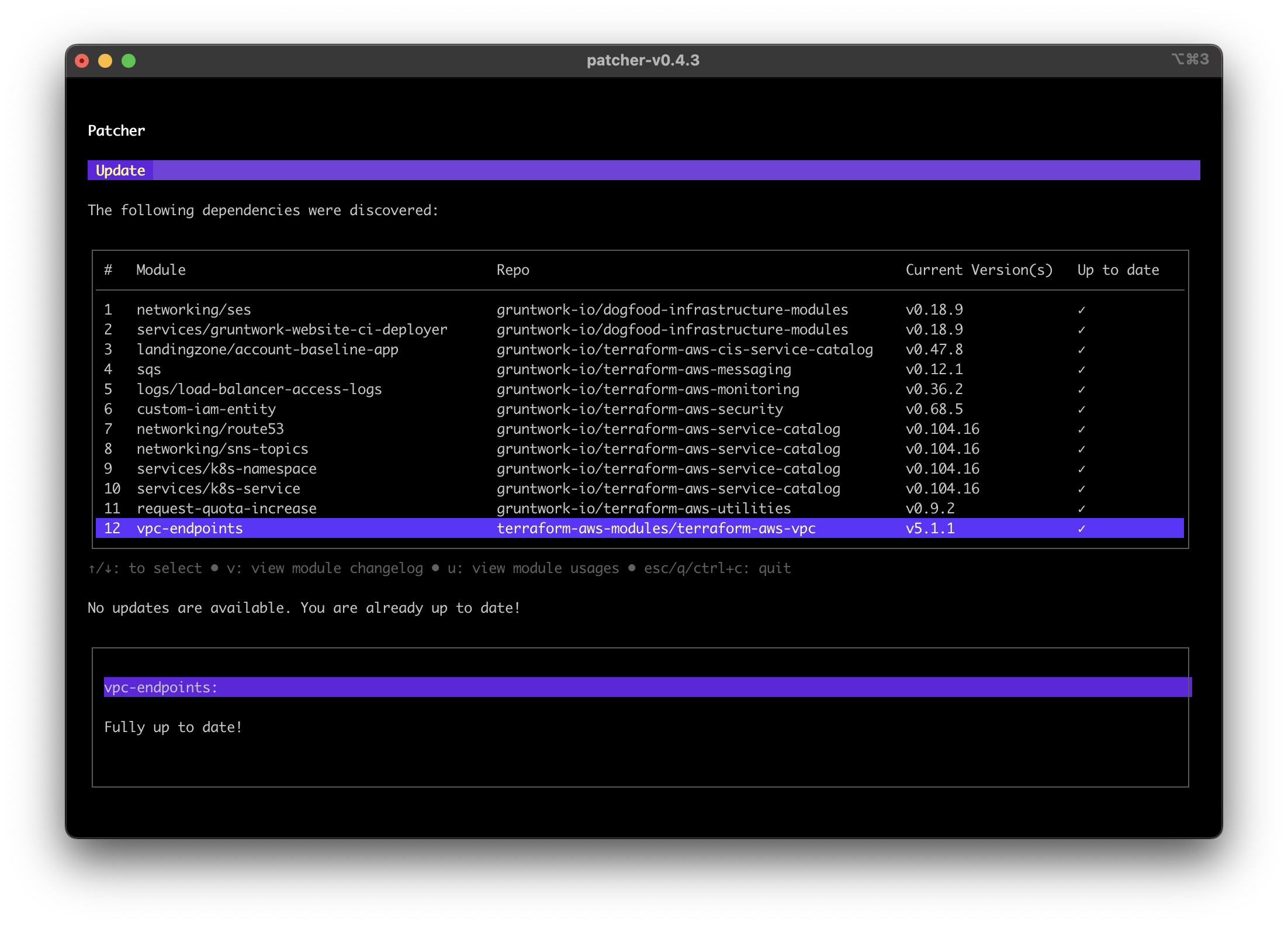 Screenshot of third party module dependency full up to date
Screenshot of third party module dependency full up to date