Running Gruntwork Drift Detection
Detecting Drift
Gruntwork Drift Detection can be executed manually or on a scheduled basis.
It is recommended to start with manual runs, focusing on individual directories of your IaC. This approach allows you to resolve drift incrementally before enabling scheduled Gruntwork Drift Detection for the entire repository.
Gruntwork Drift Detection Filter
The Gruntwork Drift Detection Filter is used to limit the units that are checked for drift. It is a comma-separated list of paths that should be included when checking for drift. The filter can be combined with the Ignore List to further limit the units that are checked for drift. The filter uses the same syntax as the Ignore List.
The Filter can contain multiple patterns separated by the , character.
,Is used as a separator between filters*Matches any character except/, for matches within a specific directory.**Matches any character, for matches across multiple directories.
Running manually
- GitHub
- GitLab
You can manually initiate Gruntwork Drift Detection by navigating to the Actions tab in your GitHub repository, selecting "Pipelines Drift Detection" from the left-hand menu, and then clicking "Run Workflow."
By default, the workflow evaluates all units in your repository and generates a pull request on the drift-detection branch. To limit drift detection to specific units, specify a path filter. For instance, to target only the management directory, use the filter management/**.
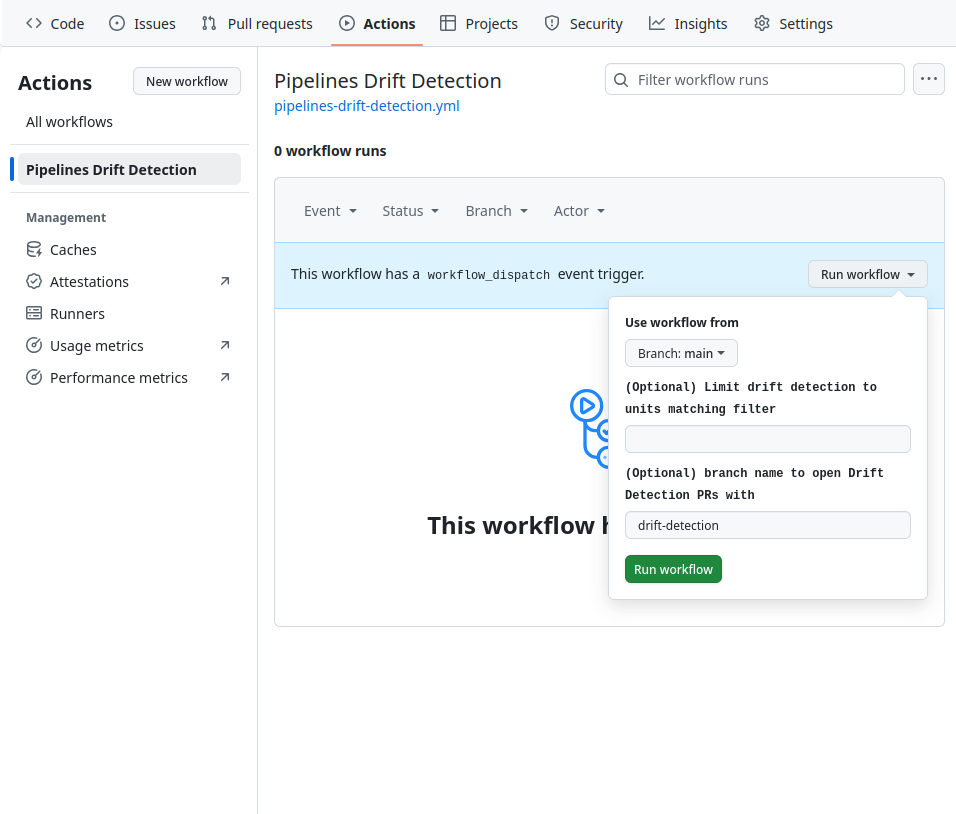 Manual Dispatch
Manual Dispatch
You can manually initiate Gruntwork Drift Detection by navigating to the Build > Pipelines section in your GitLab project and clicking "New pipeline".
Under Inputs change the "pipelines_workflow" input to "drift-detection".
By default, the workflow evaluates all units in your repository and generates a merge request on the drift-detection branch. To limit drift detection to specific units, set the pipelines_drift_detection_filter input. For instance, to target only the management directory, set the variable to management/**.
Click "New pipeline" to run the workflow.
Running Gruntwork Drift Detection on a large repository can take a long time and use a significant amount of GitLab compute minutes. If the configured GitLab job duration is exceeded, the job will be cancelled. We recommend using the Filter input to limit the units that are checked for drift.
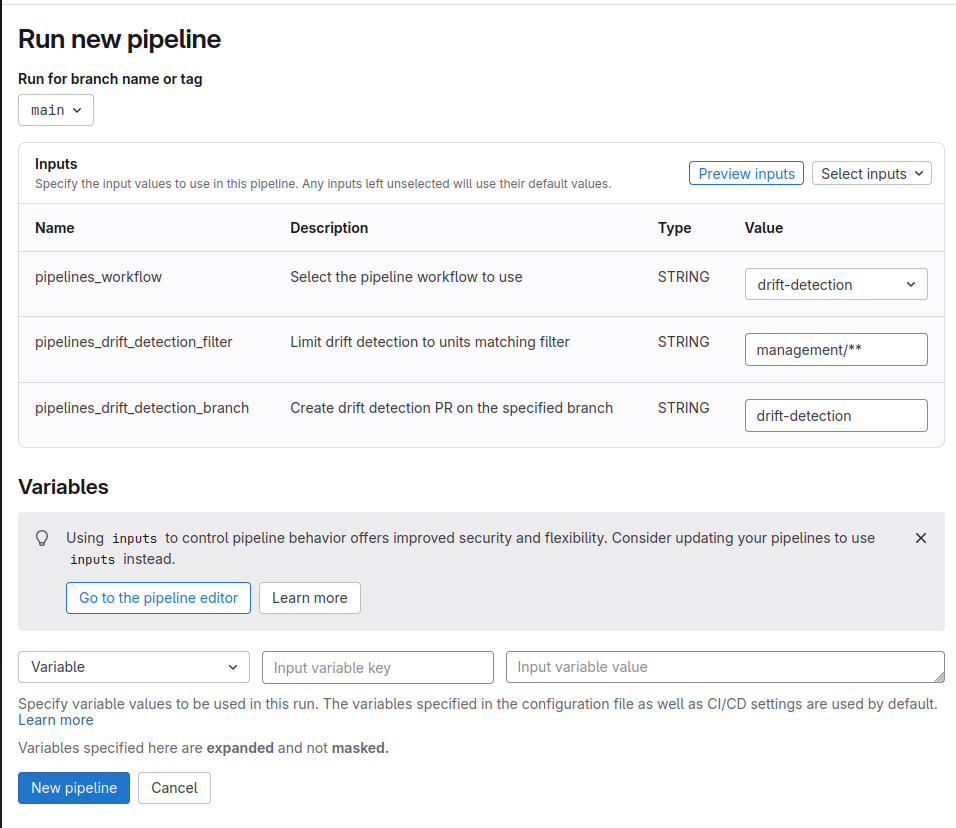 Manual Dispatch
Manual Dispatch
Running on a schedule
- GitHub
- GitLab
To enable scheduled runs:
- Uncomment the
scheduleblock in.github/workflows/pipelines-drift-detection.ymlthat contains- cron: '15 12 * * 1'. - Adjust the cron schedule to reflect your preferred frequency. The default configuration runs at 12:15 UTC every Monday. Use crontab syntax to customize the timing.
- Each Gruntwork Drift Detection run creates a pull request in your repository. If an existing Gruntwork Drift Detection pull request remains unmerged, it will be updated or replaced.
Running Gruntwork Drift Detection too frequently can consume a significant number of GitHub Action minutes. Begin with a lower frequency and adjust as needed based on your usage patterns.
To create a scheduled run:
- Navigate to Build > Pipeline schedules in your GitLab project
- Click "Create a new pipeline schedule"
- Provide a description and choose the interval for the schedule
- Under Inputs use the Select inputs drop down to add the "pipelines_workflow" input
- Change the "pipelines_workflow" input to "drift-detection"
- Optionally, add the "pipelines_drift_detection_filter" input and set it to your desired path filter
- Click "Create pipeline schedule"
Running Gruntwork Drift Detection too frequently can consume a significant number of GitLab CI/CD minutes. Begin with a lower frequency and adjust as needed based on your usage patterns.
Resolving Drift
Drift can be addressed by either applying the current IaC configuration from your repository or modifying the modules to match the infrastructure state in the cloud.
Merging the drift request
Merging the pull/merge request triggers a terragrunt apply on the modules identified as having drift.
Updating units
Alternatively, modify the drifted modules to align them with the desired state and commit the changes to the drift-detection branch. Each change triggers a new terragrunt plan for the affected units, which you can review to ensure the drift is resolved.
When the pull/merge request is merged, Pipelines will execute terragrunt apply on all drifted or modified units. If a unit no longer exhibits drift, the apply operation will result in no changes being made to the infrastructure.